Remote patient monitoring devices enable healthcare personnel to monitor their patients’ conditions outside the clinic setting remotely. This technology gives patients control over their health while lowering the cost and timing of providing Medicare. RPM devices work by electronically transmitting data about the patient to healthcare providers for evaluation, recommendations, and additional instructions if needed.

Even before the covid 19 pandemic, RPM devices were gaining popularity. The pandemic has only demonstrated the importance of this type of health care when patients are incapacitated or unable to move due to physical or geographical constraints. It can also reduce the number of in-patients and length of stay, easing the strain on an already overburdened medical system.
To highlight these advantages, among many others, is one of the reasons we put together this extensive list of monitoring medical devices for any healthcare provider.
What is remote patient monitoring (RPM)?
Remote Patient Monitoring falls under the category of homecare telehealth. This program allows physicians to gather data (Patient generated health data) from the patient using technology and remote medical devices. Physiological information that can be gathered with RPM programs includes; heart rate, blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and weight.

Once data has been gathered, patient data is transmitted to a doctor’s office using a specialized digital telehealth system or software program that can be downloaded and installed on a computer, cellphone, or iPad.
How does remote health monitoring system work?
RPM employs digital technology to collect medical and health data from patients being monitored either in a hospital or at home. The system securely transmits the information to healthcare providers in a digital form.
The following is a step-by-step explanation of how RPM works.
Step 1: Collection of data
The procedure begins with the activation of the patient monitor. A wireless transmitter measures defined physiological parameters and stores the information it collects. The information is then formatted for transmission to the patient’s healthcare provider.
Step 2: Transmission
Once the RPM device records the patient’s health data and sends it to a relational database via a specific smartphone app, it is transmitted to the appropriate healthcare provider. The accuracy of the medical information gathered and the speed with which it can be sent to the appropriate hospital or health professional has dramatically improved in recent years. There has been a significant improvement in the accuracy of data collected, and the speed with which it can be sent to the appropriate medical facility or health professional has dramatically improved in recent years.
Modern RPM devices can analyze real-time data, making it easier to identify abnormal readings. The health information is then sent to the medical facility using cutting-edge technology, such as the internet, emails, or smartphones.
Step 3: Evaluation
Medical experts will review data and identify potential health abnormalities after data transmission. The patient or their healthcare team will be notified about the patient’s conditions. The medical staff will know how to respond and contact the patient based on their data.
Step 4: Responding to the situation
If necessary, the RPM systems will alert emergency responders if immediate action is required. The medical team is informed, and first aid is given if the patient’s health information suggests they need immediate medical attention. The doctor can inform the patient via various communication channels, such as email, calls, or in-app notifications if the data suggests that a change in treatment is necessary. The medical team can advise the patient on preventing unpleasant conditions from occurring again.

Top 10 RPM devices 2022
Here are a few available remote patient monitoring tools and telemonitoring devices.
1. Blood pressure monitor
Doctors can monitor and treat hypertension/high blood pressure using blood monitoring devices. They also prevent false blood pressure readings caused by “white-coat hypertension.”
2. Glucometer
With the use of a test strip that is attached to the glucometer, a patient’s blood sugar is measured. A tiny drop of blood from the patient is applied to the test strip, and the meter reads it to generate the sugar levels reading. The glucometer aids in understanding how specific elements are affecting the patient’s glucose levels and diabetic complications.
3. Weight monitor
Remote weight monitoring ensures that any sudden, rapid weight gain or reduction is instantly recognized. The hazards of abrupt weight loss, such as a weakened immune system, dehydration, and exhaustion, can be addressed immediately by practitioners.

4. ECG + Stethoscope
A stethoscope measures heart and lung vibrations, while an ECG records heart function. Patients with heart disorders, including arrhythmias or coronary heart disease, frequently use the ECG. Using a stethoscope allows a healthcare professional to hear the heartbeat, respiratory, and bowel sounds by amplifying the sound.
5. Thermometer
A quick and precise reading of the patient’s fever (body temperature) using a Bluetooth thermometer gives the healthcare professional crucial information to guide the subsequent stages in providing care.
6. Wearable sensors for remote health monitoring
These wearable are attached to the patient’s body to provide ongoing symptom and biometric tracking. A patient’s heart rate, sugar level, and stress can all be monitored with a single wearable. Information from the activity can be used by physicians to guide the patient’s care plan.
7. Pulse Oximeter
This device is a non-invasive clip that measures blood oxygen levels. It is fixed to the patient’s finger or, in rare circumstances, earlobe. The device records the patient’s heartbeat as well.
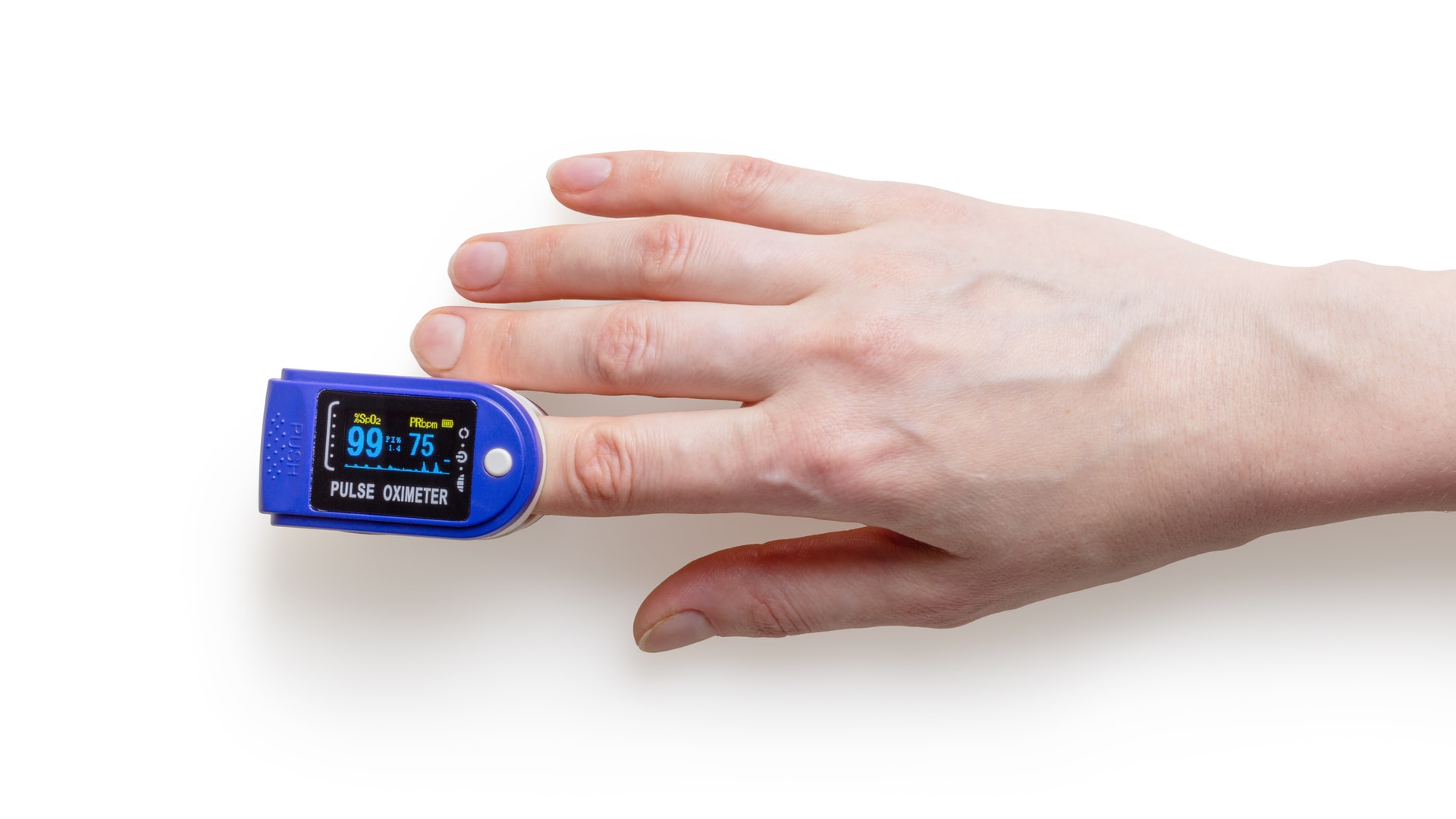
A pulse oximeter is used daily for chronic illnesses like heart or lung conditions.
8. Spirometers
The amount of air a person may inhale or exhale and spirometers measure its flow. Assessment and monitoring of illnesses, including respiratory conditions, as well as the diagnosis of asthma, depend heavily on spirometry testing.
9. AI Computer Vision
Many industries, including healthcare, have benefited from telehealth monitoring devices and artificial intelligence (AI). It is anticipated to improve computer vision. With this technology, machines will be able to diagnose complications more quickly than people. Estimating blood loss in women during and after childbirth is one example of its application.

10. Micro sampling Devices
This portable gadget, which has been available on the market for some time, makes it easier for patients to collect blood at home. Furthermore, this remote sampling technique simplifies sample collection in areas with limited resources and is more cost-effective.
Conclusion
RPM healthcare, in essence, is a quick and reliable approach for medical professionals to monitor a patient’s chronic medical issues anywhere closely they are. If you still need convincing about the benefits of RPM, consider some of the most recent software applications that are powering it and how helpful they have been.